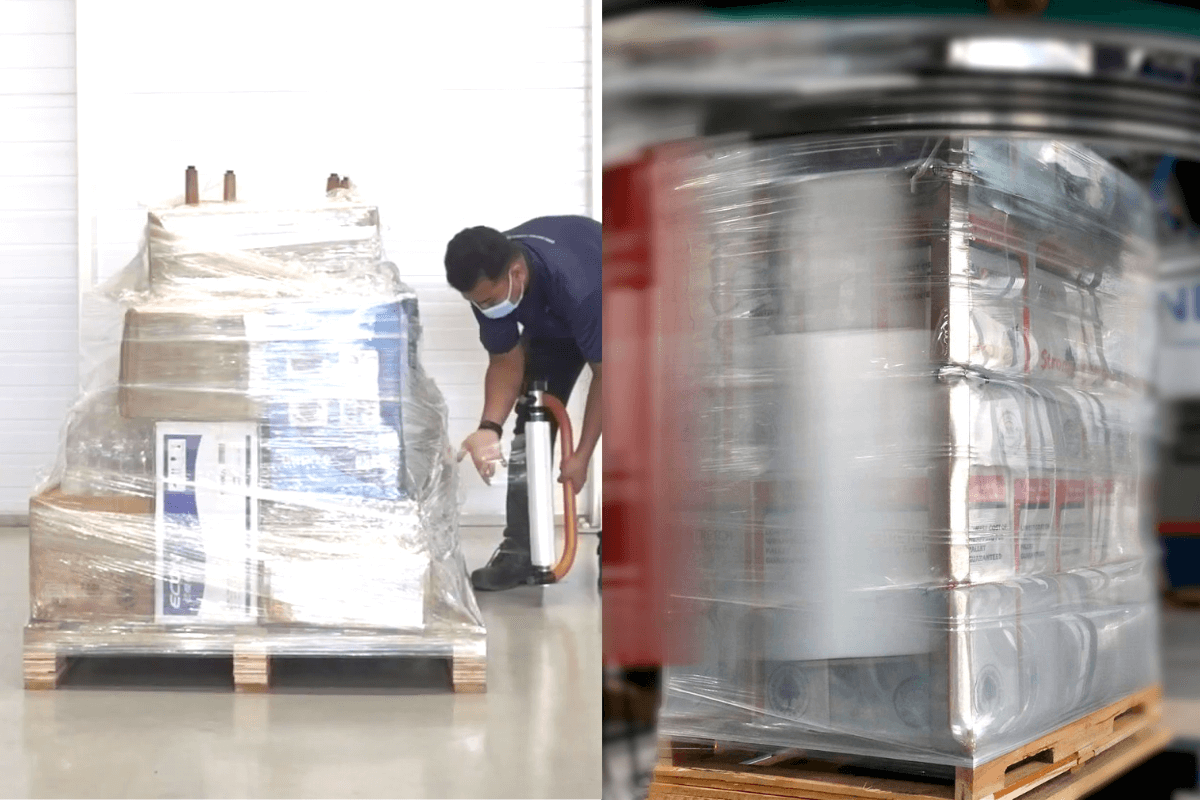
When it comes to securing pallet loads, the method you choose matters. It affects not just how well your goods are protected, but also how efficient and cost-effective your operation can be. Two common approaches are hand wrapping and stretch wrapping, each with their own pros and cons depending on your business needs.
In this guide, we’ll break down the differences between the two, explain when each makes the most sense, and offer practical tips to help buyers get the most out of their stretch film, whether you’re using a manual dispenser or a more automated system.
What Is Hand Wrapping?
Hand wrapping is a manual process where stretch film is applied to a pallet by hand—often with the help of a dispenser to make things easier and more consistent. It’s a widely used method, especially in smaller operations or when wrapping fewer pallets per day.
Why Some Businesses Prefer It:
- Minimal upfront cost
- No electricity or machinery required
- Easy to use and set up in tight spaces or temporary packing zones
That said, hand wrapping can vary in effectiveness depending on how it’s applied. With the right technique and tools—such as a stretch film dispenser—it’s possible to achieve consistent wraps while minimizing strain on the user.
As with any manual process, results can differ based on experience, but many operations continue to rely on hand wrapping effectively, especially when paired with the right setup and training.
What About Stretch Wrapping?
When people refer to stretch wrapping, they’re often talking about using a semi-automatic or fully automatic machine to apply stretch film around a pallet. These machines are designed to wrap consistently and quickly with minimal manual labor.
Where It Excels:
- Maintains consistent film tension and application
- Speeds up the wrapping process significantly
- Reduces physical strain on workers
- Can lead to long-term savings through efficient film usage
Stretch wrapping machines are a bigger investment up front, but they’re often worth considering for businesses wrapping dozens of pallets daily or looking to scale.
Comparing Hand Wrapping vs. Stretch Wrapping
Here’s a side-by-side overview to help you evaluate which might suit your operations better:
Aspect | Hand Wrapping | Stretch Wrapping |
Speed | Slower, manual pace | Fast and automated |
Consistency | Depends on user skill | Consistent and repeatable |
Labor Effort | Physically demanding | Low effort |
Cost | Low initial cost | Higher initial investment |
Best For | Lower volumes, irregular loads | High volumes, standard loads |
Making Hand Wrapping More Efficient
If you’re using hand wrapping and want to get better results, there are a few key areas to focus on.
1. Choosing the Right Hand Roll Stretch Film
Not all stretch films are created equal. Consider the following:
- Thickness (Gauge): Thicker films handle heavier loads, while thinner options may be more cost-effective for lighter items.
- Pre-stretched Film: Requires less force to apply, which can reduce fatigue and improve consistency.
- Clarity and Stickiness: High clarity helps with scanning and load checks. Some films have cling on one side to prevent pallets from sticking together.
2. Using a Stretch Film Dispenser
A dispenser helps control film tension, reduces strain on the user, and speeds up the process. It’s a simple tool that can make a big difference—especially if you’re wrapping multiple pallets a day.
When Stretch Wrapping Machines Make Sense
If you’re wrapping a lot of pallets daily—let’s say more than 15 to 20—it might be time to look at semi- or fully automatic machines. They reduce physical strain, save time, and help cut down on film waste by applying just the right amount every time.
Machines aren’t always the answer for every operation, but they’re worth evaluating as part of a long-term growth plan—especially if consistency and speed are becoming bottlenecks.
Best Practices for Using Stretch Film Effectively
Regardless of whether you’re wrapping by hand or using a machine, following a few key best practices can significantly improve your results. It all starts at the base—anchoring the film securely to the bottom of the pallet helps stabilize the load and ensures the wrap holds everything tightly in place during transport.
As you work your way up the pallet, maintaining a consistent overlap—ideally around 50%—is important. This ensures that each layer reinforces the one before it, helping to create a secure and uniform wrap across the entire load. For those using standard stretch film (as opposed to pre-stretched film), applying a slight amount of stretch during the wrap process activates the film’s memory, which improves containment and tension.
It’s also worth noting that using more film doesn’t always translate to better protection. Over-wrapping can lead to unnecessary material usage without improving load stability. In fact, applying too many layers can sometimes cause issues, such as film bunching or product crushing. Striking a balance between enough coverage and efficient usage is key.
Lastly, no matter which method or tools you’re using, proper training plays a vital role. Ensuring that your team understands correct wrapping techniques can lead to more consistent results, reduce material waste, and prevent injuries from repetitive strain. With the right knowledge and equipment—such as a quality stretch film dispenser—even manual hand wrapping can become a reliable and cost-effective part of your packaging process.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between hand wrapping and stretch wrapping depends on a few key factors: your daily volume, available space, labor capacity, and long-term goals.
Hand wrapping offers flexibility and lower upfront costs, while stretch wrapping provides speed and consistency for growing operations. And for those somewhere in between, improved manual tools can help make the most out of your existing workflow.
Whatever your setup, optimizing your stretch film use—whether through better materials, tools, or techniques—can have a noticeable impact on efficiency, cost control, and overall packaging quality.